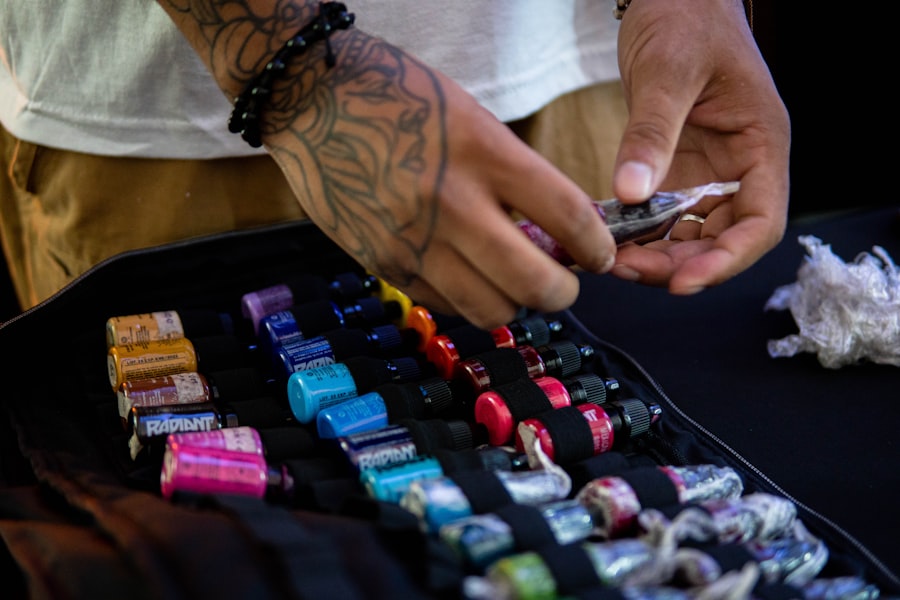
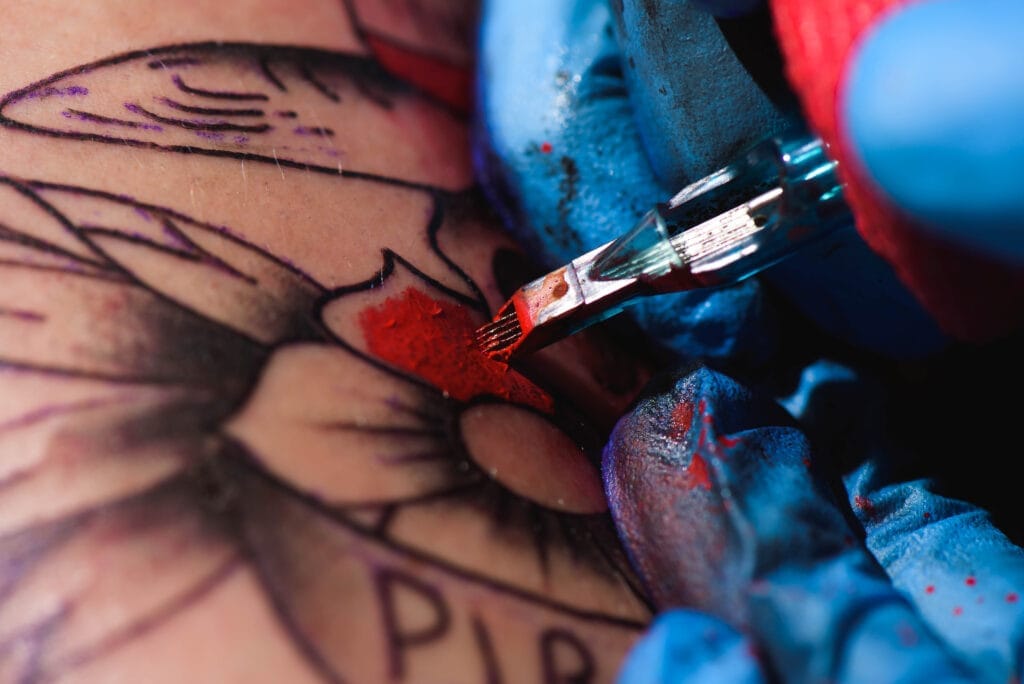
Tattoo ink is a complex mixture of various components that work together to create the vibrant designs that adorn the skin. At its core, tattoo ink consists of pigments suspended in a carrier solution. The pigments provide the color, while the carrier helps to deliver the pigments into the skin during the tattooing process.
Understanding the chemistry behind tattoo ink is essential for both artists and clients, as it can influence the quality, longevity, and safety of a tattoo. The chemistry of tattoo ink is not just about color; it also involves the interaction of these components with the skin. When a tattoo needle punctures the skin, it creates micro-wounds that allow the ink to penetrate the dermis, the second layer of skin.
The composition of the ink and its interaction with skin cells can affect how well the tattoo heals and how vibrant it remains over time. Therefore, a solid grasp of tattoo ink chemistry is crucial for ensuring that tattoos are not only aesthetically pleasing but also safe and durable.
Key Takeaways
- Tattoo ink is composed of pigments, carriers, and additives that determine its color and properties.
- The interaction between tattoo ink and the skin involves the injection of ink into the dermis layer, where it becomes encapsulated by immune cells.
- Pigments in tattoo ink are responsible for the color and stability of the tattoo, and can be organic or inorganic in nature.
- Chemical reactions during tattooing involve the breakdown of pigments by the immune system and the encapsulation of ink particles.
- Potential risks and allergies associated with tattoo ink include infections, allergic reactions, and the presence of toxic metals in some inks.
Understanding the Composition of Tattoo Ink
The Role of Pigments
Pigments are responsible for the color of the ink and can be derived from various sources, including organic materials, metals, and synthetic compounds. Each pigment has unique properties that affect its stability, lightfastness, and how it interacts with skin. For instance, some pigments may fade more quickly when exposed to sunlight, while others may remain vibrant for years.
The Importance of Carriers
The carrier solution plays a vital role in ensuring that the pigments can be effectively delivered into the skin. Common carriers include water, glycerin, alcohol, and witch hazel. These substances help to dissolve or suspend the pigments, allowing for smooth application during the tattooing process. Additionally, carriers can influence the viscosity of the ink, which affects how easily it flows from the needle and how well it adheres to the skin.
Understanding Ink Components for Quality Tattoos
Understanding the components of tattoo ink is essential for tattoo artists who want to create high-quality work that stands the test of time. By knowing how pigments and carriers interact, artists can choose the right ink for their designs and ensure that their work remains vibrant and long-lasting.
How Tattoo Ink Interacts with the Skin
When tattoo ink is injected into the skin, it does not simply sit on the surface; rather, it interacts with various layers of skin cells. The primary target for tattoo ink is the dermis, which is located beneath the epidermis. The dermis contains connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerve endings, making it an ideal location for ink to reside permanently.
The process of tattooing involves puncturing the skin repeatedly with a needle, which creates small wounds that allow the ink to enter. Once in the dermis, the body’s immune system responds to the foreign particles in the ink. Macrophages, a type of white blood cell, attempt to engulf and remove these particles.
However, many pigments are too large for macrophages to eliminate completely. As a result, some of these pigment particles remain trapped within the dermal layer, leading to a permanent design on the skin. This interaction between tattoo ink and skin cells is crucial for understanding how tattoos heal and why they can sometimes change in appearance over time.
The Role of Pigments in Tattoo Ink
Pigments are arguably the most critical component of tattoo ink, as they determine not only the color but also the overall quality and longevity of a tattoo. There are two primary categories of pigments used in tattoo inks: organic and inorganic. Organic pigments are typically derived from carbon-based compounds and can produce vibrant colors but may be less stable over time.
In contrast, inorganic pigments are often made from minerals and tend to be more durable and resistant to fading. The choice of pigment can significantly impact a tattoo’s appearance and longevity. For example, black inks often contain carbon black, which provides deep saturation and excellent lightfastness.
On the other hand, colored inks may contain various metal oxides or synthetic dyes that can produce a wide range of hues but may also pose risks for allergic reactions or fading. Understanding these differences allows tattoo artists to make informed decisions about which inks to use based on their desired outcomes and client preferences.
The Chemical Reactions Involved in Tattooing
The process of tattooing involves several chemical reactions that occur both during and after ink application. When a needle punctures the skin, it creates micro-wounds that trigger an inflammatory response in the body. This response includes the release of various chemicals that signal immune cells to migrate to the site of injury.
As macrophages attempt to engulf pigment particles in the ink, they may also release enzymes that can break down some components of the ink. Additionally, some pigments may undergo chemical changes when exposed to light or air over time. For instance, certain organic pigments can oxidize or degrade when exposed to UV radiation from sunlight, leading to fading or discoloration.
Understanding these chemical reactions is essential for both artists and clients who want to ensure that their tattoos maintain their intended appearance throughout their lifespan.
Potential Risks and Allergies Associated with Tattoo Ink
While tattoos are generally considered safe when performed by professional artists using high-quality inks, there are potential risks associated with tattoo ink that clients should be aware of. One significant concern is allergic reactions to specific pigments or additives in the ink. Some individuals may develop hypersensitivity to certain components, leading to symptoms such as itching, redness, or swelling at the tattoo site.
In addition to allergic reactions, there are also concerns about contamination during the tattooing process. If proper hygiene practices are not followed, there is a risk of introducing bacteria or other pathogens into the skin, which can lead to infections or other complications. It is crucial for clients to choose reputable tattoo shops like Redemption Ink in San Diego that prioritize safety and cleanliness to minimize these risks.
Advances in Tattoo Ink Technology
The field of tattoo ink technology has seen significant advancements in recent years, driven by a growing demand for safer and more effective products. One notable trend is the development of vegan and cruelty-free inks that avoid animal-derived ingredients and have been tested for safety without harming animals. These inks often use plant-based pigments and natural carriers, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Moreover, innovations in pigment formulation have led to improved lightfastness and stability in tattoo inks. Manufacturers are now able to create inks that resist fading over time while maintaining their vibrancy. Additionally, advancements in nanotechnology have allowed for smaller pigment particles that can provide more precise application and better integration into the skin.
These technological improvements enhance both the aesthetic quality and safety profile of tattoos.
The Future of Tattoo Ink Chemistry
As research continues into tattoo ink chemistry, we can expect further developments that will enhance both safety and performance. One area of focus is on creating inks that are less likely to cause allergic reactions or adverse effects on the skin. Scientists are exploring alternative pigments and carriers that minimize potential risks while still providing vibrant colors.
Furthermore, as consumer preferences evolve, there may be an increased demand for customizable inks that allow clients to choose specific shades or effects tailored to their individual tastes. This could lead to innovations in color-mixing technology or even smart inks that change color based on environmental factors such as temperature or light exposure. In conclusion, understanding tattoo ink chemistry is essential for both artists and clients alike.
From its composition and interaction with skin to potential risks and future advancements, knowledge in this area can lead to safer practices and more satisfying outcomes for those who choose to adorn their bodies with tattoos. As technology continues to evolve, we can look forward to a future where tattoos are not only beautiful but also safer and more personalized than ever before.
FAQs
What is tattoo ink made of?
Tattoo ink is made of pigments, carrier fluids, and other additives. The pigments are the colored particles that give the ink its color, while the carrier fluids help the ink flow and stay in liquid form.
What are the common pigments used in tattoo ink?
Common pigments used in tattoo ink include carbon black, iron oxide, titanium dioxide, and various organic pigments. These pigments are chosen for their stability and ability to produce vibrant colors.
What are carrier fluids in tattoo ink?
Carrier fluids in tattoo ink are typically made of water, alcohol, glycerin, or a combination of these. These fluids help the pigments flow evenly and stay suspended in the ink, making it easier for the tattoo artist to work with.
Are there any health concerns related to tattoo ink chemistry?
Some tattoo inks may contain heavy metals, organic compounds, or other potentially harmful substances. While many tattoo inks are considered safe, there is a risk of allergic reactions or other adverse effects. It’s important to choose a reputable tattoo artist and discuss any concerns with them before getting a tattoo.
How do different colors of tattoo ink get their hues?
The hues of different colors in tattoo ink are achieved by using specific pigments. For example, carbon black produces black ink, while iron oxide produces red, brown, and yellow inks. Organic pigments are used for a wide range of colors, and titanium dioxide is used to create white ink.